Chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for the green hues of plants, plays a crucial role in photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy. However, have you ever wondered what event accompanies energy absorption by chlorophyll? Understanding this mechanism is like unraveling a captivating mystery within the realm of plant biology. In this blog, we delve into the fascinating world of chlorophyll and explore the intricate process that unfolds alongside its energy absorption. Join us as we uncover the secrets behind this essential component of photosynthesis and gain a deeper insight into the wonder of nature’s energy conversion system.
Introduction to Chlorophyll and Energy Absorption
Chlorophyll is a vital pigment responsible for the absorption of light energy in plants during the process of photosynthesis. This green pigment is found in the chloroplasts of plant cells and plays a crucial role in converting sunlight into chemical energy that can be used by plants for growth and development.
The Role of Chlorophyll in Energy Absorption
When light strikes a chlorophyll molecule, it excites the electrons within the pigment, causing them to jump to a higher energy level. This process is the first step in the conversion of light energy into chemical energy, which is then used to drive the photosynthetic reactions.
The absorbed energy is utilized to split water molecules into oxygen and hydrogen atoms, releasing oxygen as a byproduct and storing the energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH).
Chlorophyll Absorption Spectrum
Chlorophyll has specific absorption peaks in the blue and red regions of the light spectrum, absorbing light most efficiently in these wavelengths. These absorption peaks correspond to the wavelengths at which chlorophyll molecules can absorb the maximum amount of energy for photosynthesis.
This image illustrates the absorption spectrum of chlorophyll, showing the wavelengths at which chlorophyll absorbs light most effectively:

Understanding the Process of Energy Absorption
When delving into the intriguing world of chlorophyll and its energy absorption processes, it is essential to comprehend what event accompanies energy absorption by chlorophyll. Chlorophyll, the green pigment found in plants responsible for photosynthesis, plays a pivotal role in capturing light energy from the sun and converting it into chemical energy. This conversion process is crucial for the sustenance of life on Earth.
The Role of Chlorophyll in Energy Absorption
Chlorophyll molecules consist of a porphyrin ring that absorbs light energy, particularly in the red and blue regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. This absorption triggers a series of complex chemical reactions within the chloroplasts of plant cells, leading to the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH).
This energy absorption process is crucial for photosynthesis, where carbon dioxide and water are converted into glucose and oxygen, fueling the growth and development of plants.
The Process of Photophosphorylation
One of the key events that accompanies energy absorption by chlorophyll is photophosphorylation, a light-dependent reaction that occurs during the light reactions of photosynthesis. In this process, the energy absorbed by chlorophyll molecules is used to phosphorylate adenosine diphosphate (ADP), converting it into ATP, the primary energy currency of cells.
Through photophosphorylation, the captured light energy is converted into chemical energy that can be utilized by plants for cellular processes, growth, and reproduction.
Exploring the Event Accompanying Energy Absorption
When discussing the process of energy absorption by chlorophyll, it is crucial to understand the event that accompanies this essential mechanism in photosynthesis. The primary event that occurs alongside energy absorption by chlorophyll is the excitation of electrons within the chlorophyll molecule.
Electron Excitation
Upon absorbing light energy, chlorophyll molecules undergo a process where electrons present in the molecule are excited to a higher energy state. This excitation is a pivotal event that initiates the transfer of energy within the chlorophyll molecule.
This energized state of electrons is temporary and leads to the initiation of the electron transport chain.
Role in Photosynthesis
The excitation of electrons is a fundamental step in the conversion of light energy into chemical energy during photosynthesis. This process allows plants to harness the energy from sunlight and convert it into glucose, which serves as a vital energy source for the plant.
- Chlorophyll captures light energy
- Energy is used to excite electrons
- Electrons move through the electron transport chain
- Production of ATP and NADPH for the Calvin cycle
Factors Influencing Energy Absorption by Chlorophyll
Chlorophyll, the green pigment found in plants, plays a crucial role in the process of photosynthesis by absorbing light energy and converting it into chemical energy. Several factors influence the absorption of energy by chlorophyll.
Light Intensity
The amount of light available to chlorophyll greatly affects its energy absorption capacity. Higher light intensity generally leads to increased energy absorption, while low light levels may limit this process.
In the presence of adequate light intensity, chlorophyll molecules can efficiently capture photons for photosynthesis.
Wavelength of Light
Chlorophyll absorbs light most effectively in the red and blue regions of the visible spectrum, while green light is least absorbed. This phenomenon explains why plants appear green to us, as they reflect green wavelengths of light.
The specific absorption peaks of chlorophyll molecules determine the wavelengths at which energy absorption is most efficient.
Temperature
Temperature can impact the energy absorption by chlorophyll as it affects the overall metabolic activity of the plant. Optimal temperatures enhance the efficiency of photosynthesis, while extreme temperatures can disrupt chlorophyll function.
Regulation of temperature is vital to ensure that chlorophyll molecules maintain their structure and function properly.
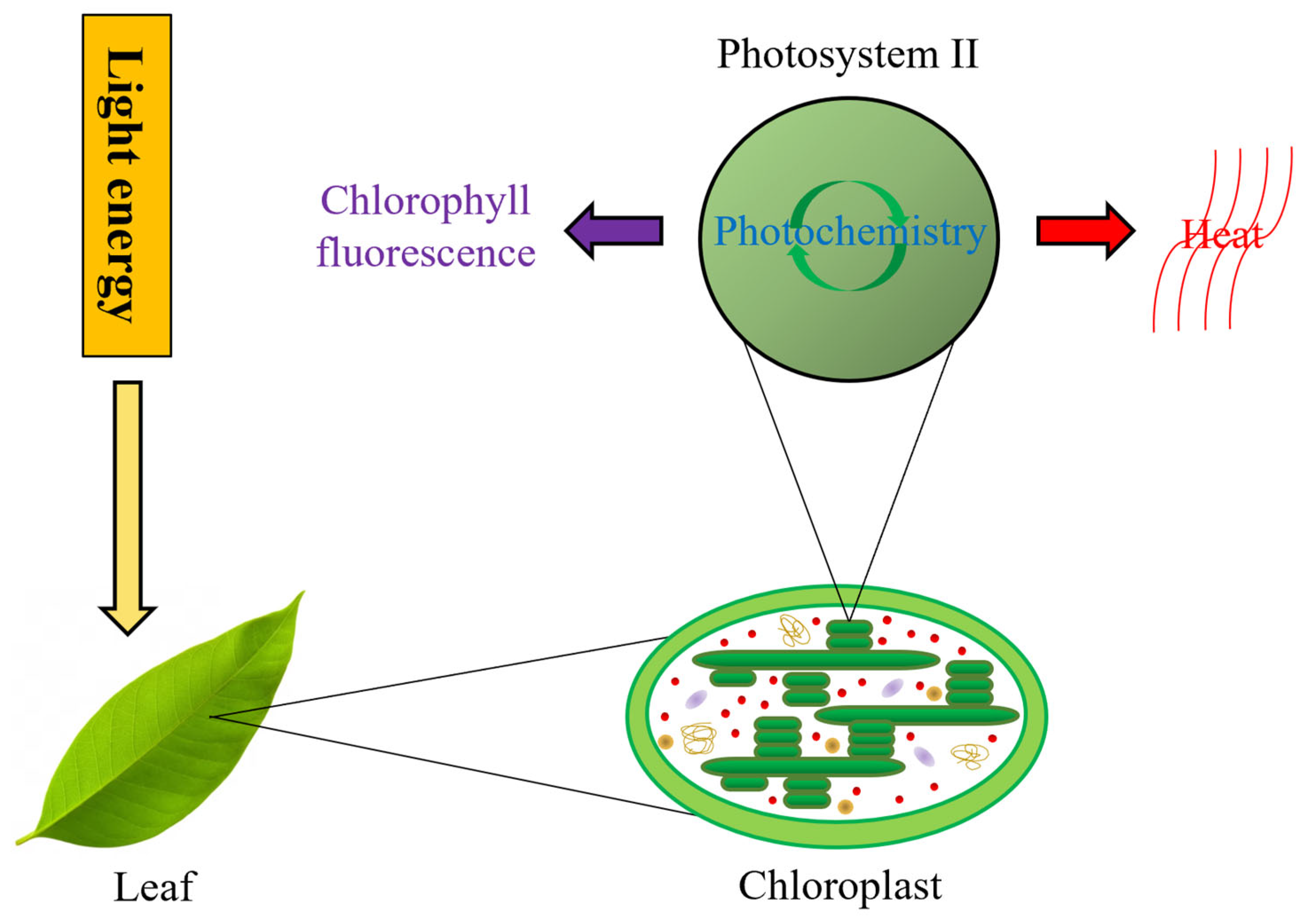
Significance of Energy Absorption in Photosynthesis
Energy absorption by chlorophyll is a crucial event in photosynthesis, the process where plants convert light energy into chemical energy. Chlorophyll, the green pigment in plants, absorbs light energy from the sun, primarily in the red and blue wavelengths, to initiate the photosynthetic process.
The Role of Chlorophyll in Energy Absorption
Chlorophyll molecules consist of a porphyrin ring that captures light energy and a hydrophobic tail that anchors it to the thylakoid membranes within chloroplasts. This unique structure allows chlorophyll to absorb and transfer energy efficiently.
Moreover, what event accompanies energy absorption by chlorophyllis the excitation of electrons within the pigment molecules, leading to the formation of high-energy states necessary for driving the photosynthetic reactions.
Photosynthetic Electron Transport Chain
Once chlorophyll absorbs light energy, it passes the energized electrons through a series of proteins and molecules in the thylakoid membrane, known as the electron transport chain. This process generates ATP and NADPH, which are essential for the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis.
- The excitation of electrons in chlorophyll
- Electron transport chain
- Generation of ATP and NADPH

Frequently Asked Questions
-
- What is chlorophyll?
- Chlorophyll is a green pigment found in plants and algae that is responsible for the absorption of light energy during photosynthesis.
-
- What event accompanies energy absorption by chlorophyll?
- The event that accompanies energy absorption by chlorophyll is the process of photosynthesis, where light energy is converted into chemical energy stored in glucose molecules.
-
- How does chlorophyll absorb energy?
- Chlorophyll absorbs energy from sunlight through a process called photoexcitation, where it captures photons of light and converts them into chemical energy.
-
- What happens to chlorophyll after it absorbs energy?
- After chlorophyll absorbs energy, it undergoes a series of chemical reactions that lead to the conversion of carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
Unraveling the Enigma: The Event Accompanying Chlorophyll’s Energy Absorption
After delving into the intricacies of chlorophyll and its role in photosynthesis, we have unveiled the mystery of what event accompanies energy absorption by chlorophyll. It is fascinating to understand that the absorption of light energy triggers a series of intricate chemical reactions, leading to the conversion of sunlight into chemical energy. This process, known as photosynthesis, is vital for the survival of plants and ultimately all life on Earth.
In conclusion, the event that accompanies energy absorption by chlorophyll is the initiation of the photosynthetic process, culminating in the production of glucose and oxygen. This remarkable phenomenon highlights the interconnectedness of all living organisms and the importance of understanding and appreciating the wonders of nature.

