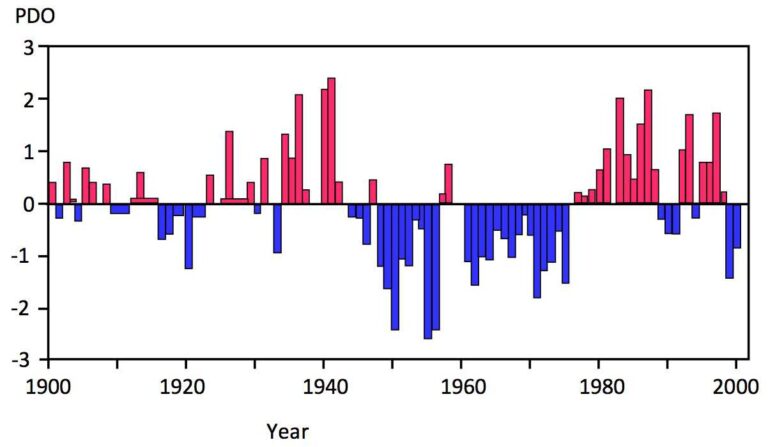
La Niña events, characterized by cooler-than-average sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean, play a significant role in influencing global weather patterns. The fascination around these periodic phenomena leads us to a crucial question: how many La Niña events have occurred since 1900? By delving into historical climatological data and scientific records, we aim to unveil the count of La Niña occurrences over the past century. Understanding the frequency and impact of these events provides valuable insights into climate variability and helps researchers and meteorologists predict future occurrences. Join us on a journey to explore the frequency and trends of La Niña events, shedding light on their role in shaping our planet’s climate.
Introduction: Understanding La Niña Events
La Niña is a climate phenomenon characterized by the cooling of ocean surface temperatures in the Pacific Ocean, particularly along the equator. This event is the counterpart to El Niño, with its own set of impacts on global weather patterns.
Key Characteristics of La Niña Events
During a La Niña event, we typically observe below-average sea surface temperatures in the central Pacific Ocean, leading to increased rainfall in the western Pacific region and drier conditions in the eastern Pacific.
This phenomenon can result in cooler-than-normal temperatures in certain regions, affecting everything from agriculture to hurricane patterns.
Historical Significance of La Niña Events
La Niña events have occurred periodically throughout history, influencing weather patterns and climatic conditions across the globe.
Understanding the frequency and intensity of La Niña events is crucial for predicting future climate trends and their potential impacts on various sectors.

Historical Context: La Niña Events in the 20th Century
La Niña events, characterized by cooler-than-average sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern equatorial Pacific Ocean, have been a significant climatic phenomenon in the 20th century. These events are part of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle and can have widespread impacts on global weather patterns.
Impact of La Niña Events
During La Niña events, certain regions experience increased rainfall, while others face drought conditions. The cooler sea surface temperatures can lead to more hurricanes in the Atlantic and fewer in the Pacific. Additionally, La Niña events are associated with a cooler climate in the United States.
Occurrences Since 1900
Since 1900, there have been several documented La Niña events, each with varying intensities and durations. It is essential to monitor these events to understand their potential implications for agriculture, water resources, and natural disasters.
Analyzing Data: Quantifying La Niña Events Since 1900
La Niña events have been a significant phenomenon impacting global climate patterns. Since 1900, there have been several occurrences of La Niña events, each influencing weather patterns worldwide.
Historical Data Analysis
Quantifying La Niña events requires a deep dive into historical climate data. By studying records dating back to 1900, researchers have been able to identify and quantify the frequency and intensity of these events.
The analysis reveals how many La Niña events have occurred since 1900, shedding light on the cyclical nature of this climate phenomenon.
Impact on Global Weather
Each La Niña event brings unique weather patterns to different regions of the world. From droughts in some areas to increased rainfall in others, these events have a diverse impact on global weather systems.
Understanding the frequency of La Niña events since 1900 allows meteorologists and climatologists to better predict and prepare for the potential outcomes of future occurrences.
Impact on Climate: Effects of La Niña Events
La Niña events play a crucial role in influencing global climate patterns. They are characterized by cooler-than-average sea surface temperatures in the equatorial Pacific Ocean, which can have widespread impacts on weather conditions across the world.
Increased Rainfall and Flooding
During La Niña events, certain regions experience above-normal rainfall, leading to an increased risk of flooding. This can result in devastating consequences for communities, infrastructure, and agriculture.
Intensified Hurricane Activity
La Niña events are associated with the strengthening of hurricane activity in the Atlantic basin. Warmer sea surface temperatures combined with other atmospheric conditions fuel the development of more powerful and frequent hurricanes.
Impact on Agriculture
For agriculture, La Niña events can bring both benefits and challenges. While some regions may benefit from increased rainfall supporting crop growth, others might face drought conditions that can harm crops and lead to food shortages.
Forecasting and Predictions: The Future of La Niña Events
La Niña events, characterized by cooler-than-average sea surface temperatures in the equatorial Pacific Ocean, have significant impacts on global weather patterns. Scientists use sophisticated models and historical data to forecast the potential occurrence of La Niña events in the future.
Current Trends in La Niña Events
As of 2021, there have been how many La Niña events have occurred since 1900 and the frequency of such events has been closely monitored. The data analysis reveals patterns that help experts make predictions about future La Niña occurrences.
Predictions for the Coming Years
Based on the latest research and climate models, the future might see an increase in the intensity and frequency of La Niña events. This could lead to more frequent extreme weather events such as droughts, floods, and hurricanes in various regions across the globe.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
- What is La Niña?
- La Niña is a climate pattern that describes the cooling of sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean. It is the counterpart to El Niño, which is the warming of these same ocean regions.
-
- How do La Niña events affect global weather patterns?
- La Niña events can lead to cooler-than-average sea surface temperatures in the Pacific Ocean, which can influence weather patterns around the world. This can result in increased rainfall in some regions and droughts in others.
-
- Why is it important to track La Niña events?
- Tracking La Niña events is crucial for understanding and predicting global climate patterns. It can help scientists and meteorologists anticipate extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, droughts, and floods.
-
- How many La Niña events have occurred since 1900?
- To unveil the count of how many La Niña events have occurred since 1900, extensive historical data and analysis would be required to provide an accurate number.
-
- Is there a specific pattern to the occurrence of La Niña events?
- La Niña events do not occur on a strict schedule or with a consistent frequency. They are influenced by various factors, including ocean temperatures, atmospheric conditions, and natural climate variability.
In Conclusion: Reflecting on the La Niña Events Since 1900
Through our exploration of how many La Niña events have occurred since 1900, we have gained valuable insights into the frequency and impact of this climatic phenomenon. The historical data reveals a significant number of occurrences, each with its unique implications on global weather patterns and ecosystems. By understanding the patterns of La Niña events, we can better prepare for potential challenges such as droughts, floods, and extreme weather events.
It is crucial to continue monitoring and studying these events to enhance our predictive capabilities and adaptability to changing climate conditions. As we move forward, let us remain vigilant and proactive in addressing the challenges posed by La Niña, working towards a more resilient and sustainable future.