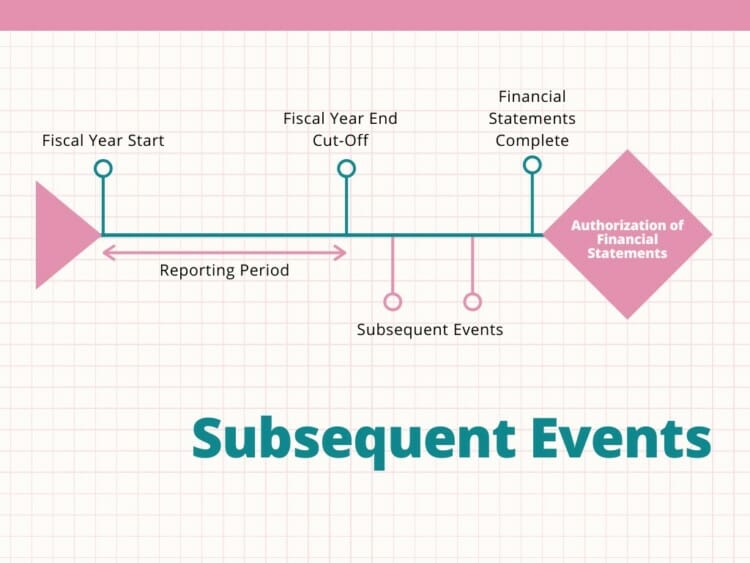
Have you ever heard the term “subsequent event” thrown around in conversations about business or finance? What exactly does it entail? In the realm of accounting and reporting, a subsequent event refers to occurrences that take place after the balance sheet date but before the financial statements are issued. These events can significantly impact the financial position of a company and may require disclosure to ensure transparency and accuracy in financial reporting.
This blog aims to delve into the depths of what constitutes a subsequent event, why it matters, and how businesses navigate the complexities surrounding them. Join us on this journey as we uncover the intricacies of subsequent events and their implications on financial decision-making.
Introduction: Understanding the Concept of Subsequent Events
In the realm of financial reporting and analysis, what is a subsequent event plays a crucial role in providing users with the most up-to-date information about a company’s financial status. Subsequent events refer to events occurring after the end of the reporting period but before the financial statements are issued. These events can significantly impact the decisions of investors, creditors, and other stakeholders.
Key Aspects of Subsequent Events
Subsequent events are classified into two categories: recognized subsequent events and non-recognized subsequent events. Recognized subsequent events are those that provide further evidence of conditions that existed at the end of the reporting period, whereas non-recognized subsequent events are those that represent new conditions arising after the reporting period.
Significance for Financial Reporting
Understanding subsequent events is crucial for ensuring the reliability and relevance of financial statements. Companies need to evaluate events occurring after the reporting period to determine if they require adjustment or disclosure in the financial statements. Failure to address significant subsequent events can lead to misleading financial information.

Importance of Identifying Subsequent Events
Identifying subsequent events is crucial in the financial world as it impacts the accuracy of a company’s financial statements. These events occur after the balance sheet date but before the financial statements are issued. They can have a significant effect on a company’s financial position and must be evaluated to ensure transparency.
Enhanced Transparency
Recognizing subsequent events enhances the transparency of financial reporting. It ensures that stakeholders have access to the most up-to-date information, enabling them to make informed decisions based on the company’s current circumstances.
Understanding what is a subsequent event allows investors and regulators to assess the impact of recent developments on a company’s financial health.
Compliance with Accounting Standards
Properly identifying subsequent events is essential for compliance with accounting standards. Failure to disclose material subsequent events can lead to non-compliance and may raise concerns about the reliability of financial statements.
Adhering to accounting guidelines ensures that financial reports accurately reflect the company’s financial position, aiding in building trust with investors and other stakeholders.
Criteria for Recognizing Subsequent Events
When dealing with financial reporting, it is essential to understand the criteria for recognizing subsequent events. These events occur after the balance sheet date but before the financial statements are issued. They can have a significant impact on the company’s financial position and must be evaluated carefully.
Timing of the Event
The first criterion to consider is the timing of the event. Subsequent events should occur between the balance sheet date and the date when the financial statements are available to be issued. Events that happen after the financial statements’ issuance are not considered subsequent events.
Nature of the Event
The nature of the event is crucial in determining whether it should be recognized. Events that provide additional information about conditions that existed at the balance sheet date are generally recognized. On the other hand, events that represent new circumstances after the balance sheet date are not recognized.
Examples of Subsequent Events in Different Industries
Subsequent events can have significant impacts on various industries. In the tech sector, the launch of a groundbreaking product like a new smartphone or software update can be considered a subsequent event. For instance, in 2021, Apple unveiled its latest iPhone model, triggering a surge in consumer interest and stock prices.
Healthcare Industry
In the healthcare industry, the approval of a new drug by regulatory authorities can be a crucial subsequent event. Pharmaceutical companies eagerly await such milestones as they directly impact revenue and market positioning. An example from 2021 includes the FDA approval of a revolutionary treatment for a rare disease, leading to a spike in the company’s shares and global attention.
Automotive Sector
For the automotive sector, a merger between two major car manufacturers could be a significant subsequent event. In recent years, Tesla’s acquisition of a leading battery technology firm in 2021 reshaped the electric vehicle market landscape. This move not only diversified Tesla’s offerings but also emphasized its commitment to sustainability and innovation.
Financial Reporting Implications of Subsequent Events
Financial reporting must accurately reflect a company’s financial position at the end of the reporting period. Subsequent events are events that occur after the reporting period but before the financial statements are authorized for issue. These events can impact the financial statements and should be carefully evaluated.
Types of Subsequent Events
Subsequent events can be categorized into two types: recognized and non-recognized subsequent events. Recognized subsequent events are those that provide additional information about conditions that existed at the end of the reporting period. Non-recognized subsequent events are those that represent new conditions that arose after the reporting period.
Reporting Requirements
Companies are required to evaluate subsequent events up to the date when the financial statements are issued. Recognized subsequent events need to be reflected in the financial statements, while non-recognized subsequent events may require disclosure in the footnotes to the financial statements. Failure to appropriately account for subsequent events can lead to misrepresentation and potential legal consequences.
Case Studies on Handling Subsequent Events
When it comes to understanding what is a subsequent event, real-time case studies can provide valuable insights. In the current year, businesses worldwide have faced unprecedented challenges due to unforeseen events.
Case Study 1: Adapting to Market Shifts
Company A faced a sudden shift in consumer behavior due to a global pandemic. By quickly adapting their marketing strategies and embracing digital platforms, they not only survived but also thrived amidst uncertainty.
Case Study 2: Supply Chain Resilience
During a supply chain disruption, Company B utilized data analytics to forecast potential risks and identify alternate suppliers. This proactive approach helped them mitigate losses and maintain customer trust.
Best Practices for Disclosure of Subsequent Events
When it comes to understanding what is a subsequent event, companies must adhere to best practices for disclosing such events to ensure transparency and compliance with regulations.
Timely Reporting
One of the key practices is ensuring timely reporting of subsequent events. Companies should disclose any significant events that occur between the end of the reporting period and the financial statements’ issuance.
Materiality Assessment
Conducting a materiality assessment is crucial to determine the impact of subsequent events on financial statements. Events considered material should be disclosed to inform stakeholders accurately.
- Assess events for their potential financial impact
- Consider events’ relevance to decision-making
Frequently Asked Questions
-
- What is a subsequent event?
- A subsequent event is an event or transaction that occurs after a company’s financial statements have been issued but before those financial statements are available to be issued.
-
- Why are subsequent events important?
- Subsequent events are important because they may have a significant impact on a company’s financial position and performance, and therefore, they may require adjustments to the financial statements or disclosures.
-
- What are the types of subsequent events?
- Subsequent events are categorized into two types – recognized subsequent events, which require adjustments to the financial statements, and non-recognized subsequent events, which require only disclosure in the financial statements.
-
- How are subsequent events disclosed in financial statements?
- Subsequent events that require disclosure are usually described in a separate note to the financial statements, providing details about the nature of the event and its potential impact on the company.
-
- Who is responsible for determining subsequent events?
- Management of the company is responsible for evaluating subsequent events and determining whether they require adjustments to the financial statements or disclosure in the notes to the financial statements.
Final Thoughts: Understanding What is a Subsequent Event
As we unravel the mystery surrounding subsequent events, it becomes clear that they provide crucial insights into a company’s financial health and performance post-reporting period. These events can have significant impacts on financial statements and must be disclosed to ensure transparency and accuracy. By recognizing the importance of identifying and evaluating subsequent events, businesses can better navigate unforeseen developments and make informed decisions. In summary, understanding what constitutes a subsequent event empowers stakeholders to assess the true picture of a company’s current standing and adapt their strategies accordingly. Stay informed, stay vigilant, and let the consideration of subsequent events be a valuable tool in your financial analysis toolkit.